2 Level Factorial Design
Consider the two-level full factorial design for three factors namely the 2 3 design. A 22 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables each with two levels on a single dependent variable.

5 3 3 3 1 Two Level Full Factorial Designs
To understand the factorial experimental design you must be well-acquainted with the following terms.

. The 2k factorial design is a s pecial case of the general factorial design. Therefore R 2 is most useful when you compare models. 18H as In Decimal.
In this type of design one independent variable has two levels and the other independent variable has three levels. 24 18H Input. For example a 2 5 2 design is 14 of a two level five factor factorial design.
High and watering frequency daily vs. R 2 is always between 0 and 100. R 2 always increases when you add additional predictors to a model.
654321 720 In Hexadecimal. For example the best five-predictor model will always have an R 2 that is at least as high as the best four-predictor model. Graphical representation of a two-level design with 3 factors.
For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs. This is a broad term used to describe the independent variable that is manipulated in the experiment by the researcher or through selection. 02D0H as In Decimal.
Graphically we can represent the 2 3 design by the cube shown in Figure 31. A Catapult Fractional Factorial Experiment. For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs.
Prerequisite 8085 program to find the factorial of a number Problem Write an assembly language program for calculating the factorial of a number using 8086 microprocessor Examples Input. The main effect of a factor refers to the change produced in response to a change in the level of the factor. This type of factorial design is widely used in industrial experimentations and is often referred to as screening design due to the.
A 23 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables on a single dependent variable. The arrows show the direction of increase. This experiment was conducted by a team of students on a catapult a table-top wooden device used to teach design of experiments and statistical process controlThe catapult has several controllable factors and a response easily measured in a classroom setting.
Rather than the 32 runs that would be required for the full 2 5 factorial experiment this experiment requires only eight runs. A design with p such generators is a 1l pl p fraction of the full factorial design. This implies eight runs not counting replications or center point runs.
K factors are being studied all at 2 levels ie. A step-by-step analysis of a fractional factorial catapult experiment. High referred as or 1 and low referred as -or -1.
4321 24 In Hexadecimal. The higher the R 2 value the better the model fits your data. Weekly on the growth of a certain species of plant.

5 3 3 9 Three Level Full Factorial Designs

Full Factorial Design For 2 Factors And 2 Levels A Design Matrix Download Scientific Diagram

2 K Factorial Design Tool Real Statistics Using Excel

5 3 3 4 3 Confounding Also Called Aliasing

Design Of Experiments Experiments Change Management Pre Med
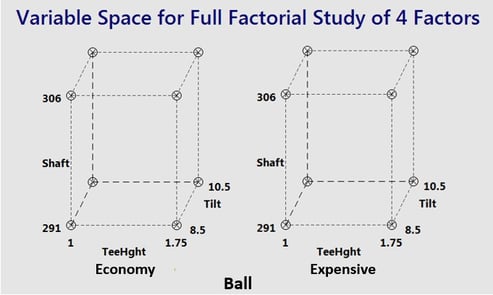
5 Reasons Factorial Experiments Are So Successful

5 3 3 9 Three Level Full Factorial Designs

Chapter 8 Experimental Design Ii Factorial Designs Ppt Download

0 Response to "2 Level Factorial Design"
Post a Comment